Joint Support Supplements
Maintaining joint health is crucial for our mobility and overall quality of life. Our joints are the connecting points between bones, providing support and aiding in movement. Over time, wear and tear on these joints can lead to discomfort, stiffness, and even pain.
Factors such as age, weight, genetics, and injuries can contribute to joint deterioration, often resulting in conditions like arthritis, osteoporosis, and bursitis, which can significantly affect our daily activities and lifestyle.
In the following sections, we will address this topic and show you how joint health supplements can help you transition from a state of pain to comfort.
Joint Support Products

Chiropractor’s Choice Glucosamine
Chiropractor’s Choice Glucosamine is a dietary supplement designed to support joint health. Its unique blend of glucosamine, chondroitin, MSM, boswellia, turmeric,bromelain, and quercetin work synergistically to support joint flexibility, ease discomfort, and enhance overall movement.
from $19.99
Table of Contents
Understanding Joint Health

A joint, in simple terms, is the point where two bones meet. It’s a complex structure composed of several different components that work together to facilitate movement and provide structural support. Here’s a brief overview of the anatomy of a joint:
Bone
These form the structure of the joint, and there are six types of freely movable joints in the body.
Cartilage
This is a type of connective tissue that covers the surface of a joint, providing a smooth, lubricated surface for articulation and serving as a shock absorber.
Synovial Fluid
Found in movable joints, this fluid provides lubrication, reduces friction, and helps distribute nutrients to the cartilage.
Ligaments
These are tough bands of tissue that connect one bone to another, stabilizing the joint and controlling the range of motion.
Tendons
Tendons connect muscles to bones, helping control movement when muscles contract.
Muscles
Muscles are responsible for making your joints move. They do this by contracting and pulling on the tendons.
Bursae
These small fluid-filled sacs reduce friction between moving parts in your body’s joints
Common Causes of Joint Pain and Degradation
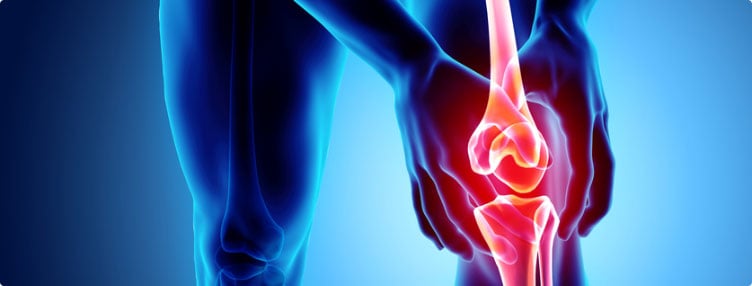
Joint pain and degradation are common issues that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. These conditions can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Aging
As we age, the cartilage in our joints naturally begins to wear down, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis.
Injury or Overuse
Injuries to joints, or simply using them excessively, can cause damage and result in pain and degradation over time.
Inflammation and diseases
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and gout are characterized by joint inflammation, leading to pain and potential joint damage.
Obesity
Extra weight puts additional pressure on weight-bearing joints like knees and hips, which can accelerate wear and tear.
Genetics
Some people are genetically more prone to certain types of joint conditions.
Lifestyle Choices Impacting Joint Health

Our lifestyle choices can impact our joint health. Here are a few key factors:
- Diet
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can support joint health. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods and sugars can contribute to inflammation and exacerbate joint issues.
- Physical Activity
Regular exercise strengthens the muscles around the joints, improving stability and reducing the strain on the joints. It’s important, however, to balance activity with rest to avoid overuse injuries.
- Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the load on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips, slowing the rate of cartilage breakdown.
- Posture and Ergonomics
Proper posture and ergonomics, both during physical activity and while at rest, can help prevent joint stress and strain.
- Smoking and Alcohol
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can exacerbate joint pain and inflammation and potentially lead to degenerative joint diseases.
- Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to inflammation, resulting in joint discomfort and stiffness.
- Joint Supplements
These supplements are often formulated with ingredients like glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to support joint health. They can help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, promote cartilage health, and improve joint function.
Why is it Important to Use Joint Support Supplements?
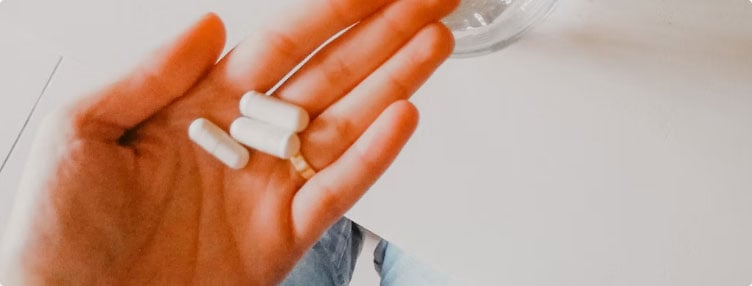
Joint support supplements are considered important for several reasons, particularly for those who suffer from joint pain or conditions like arthritis.
- Relieve Joint Pain
Supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin are known to relieve pain caused by conditions such as arthritis. They have the potential to slow cartilage deterioration in the joints, reducing pain in the process.
- Reduced Inflammation
Certain supplements can help reduce inflammation in the joints, which is a major cause of joint pain and discomfort.
- Promotion of Cartilage Synthesis
Joint supplements often contain ingredients that promote cartilage synthesis, which can help maintain the health and function of your joints.
Natural Aging and Joint Health
Natural aging is another factor that impacts joint health. As we age, the normal wear and tear on our joints can lead to a gradual loss of cartilage—the firm, rubbery material that cushions the ends of bones in joints. This process can result in conditions like osteoarthritis, a common form of arthritis characterized by the degeneration of joint cartilage and the underlying bone.

Here’s how aging can impact our joints:
Prebiotics are specialized plant fibers that act as nourishment for probiotics, which are the beneficial bacteria in your gut. The human body does not digest this dietary fiber, but it can be broken down and consumed by probiotic bacteria.

Decreased Cartilage
Loss of Muscle Mass

Reduced Flexibility

Bone Changes

Inflammation
Athletes, Fitness Enthusiasts, and Joint Care
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts often place a lot of stress on their joints due to the physical demands of their activities. This can lead to higher risks of joint injuries and conditions such as tendonitis, sprains, and strains. Therefore, joint care becomes an essential part of their routine.

Warm-Up and Cool-Down:
Warming up before exercise prepares the joints for activity by increasing blood flow and flexibility. Cooling down afterward helps to gradually reduce the heart rate and relax the muscles, minimizing post-exercise stiffness and soreness.
Proper Technique:
Using proper form during workouts is crucial to prevent unnecessary strain on the joints. It’s often beneficial to work with a trainer or coach to ensure the correct technique.


Cross-Training:
Engaging in various exercises can help evenly distribute the impact of physical activity across different joints, reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
Strength Training:
Building muscle helps to support and protect joints. Focusing on strengthening the muscles around your most used joints can significantly reduce the risk of injury.


Rest and Recovery:
Giving the body adequate time to rest and recover after intense workouts is crucial to prevent overuse injuries. This includes getting enough sleep, which is when most muscle repair and recovery happens.
Nutrition and Supplements:
Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support joint health. Additionally, joint supplements, often containing ingredients like glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help maintain cartilage health, reduce inflammation, and support overall joint function.


Hydration:
Staying hydrated helps maintain the lubrication of the joints, which is important for reducing friction and preventing wear and tear.
Regular Check-ups:
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect any potential joint issues early and keep track of the overall well-being of an athlete or fitness enthusiast.
Addressing Nutritional Gaps for Joint Maintenance
A balanced and nutritious diet is a cornerstone of joint health. However, it’s not always easy to get all the necessary nutrients from diet alone, and that’s where addressing nutritional gaps comes into play.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
These essential fats, found in fatty fish like mackerel and salmon, possess anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit joint health. If your diet lacks these foods, fish oil supplements may be beneficial.
- Vitamin D3 and Calcium:
Vitamin D3 aids in calcium absorption, which is crucial for bone health. You may need a supplement if you don’t get enough sunlight (which helps the body produce vitamin D) or consume enough dairy or fortified foods.
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin supplements
These compounds are found naturally in cartilage. While they can be consumed through certain foods like bone broth, getting therapeutic amounts from diet alone is difficult. Oral supplements can help fill this gap.
- Antioxidants
Vitamins C and E, selenium, and other antioxidants help combat oxidative stress that can contribute to joint degradation. If your diet lacks fresh fruits and vegetables, consider an antioxidant supplement.
- Turmeric and Ginger
These spices have potent anti-inflammatory effects but are usually consumed in small amounts. Supplements can offer a concentrated dose.
Key Ingredients in Joint Support Supplements
Specifically formulated to support the health and function of our joints, these dietary supplements contain a variety of ingredients that have been researched for their potential benefits to joint health.
The key ingredients typically aim to reduce inflammation, promote cartilage synthesis, improve collagen production, and relieve joint or arthritis pain.
They are often used as part of a comprehensive approach to joint health, alongside a healthy diet, regular exercise, and other lifestyle modifications. However, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of these supplements can vary from person to person, and they should always be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Glucosamine
Glucosamine is often used to help manage painful joints, especially in people with osteoarthritis, a type of arthritis that occurs when cartilage wears down over time. More recent data suggest that glucosamine sulfate may be effective in the primary prevention of osteoarthritis in sportsmen. Additionally, early research suggests that oral use of glucosamine might reduce pain linked to rheumatoid arthritis.
Chondroitin
Chondroitin is another key ingredient found in dietary supplements, and it’s an essential part of cartilage. It has been found to prevent cartilage from breaking, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals with osteoarthritis.
In fact, chondroitin supplements are used as an alternative medicine to treat osteoarthritis. Chondroitin sulfate is known to prevent joint space narrowing and reduce joint swelling and effusion by eliciting an anti-inflammatory effect at the chondral and synovial levels.
Methylsulfonylmethane
Methylsulfonylmethane, more commonly known as MSM, can reduce inflammation and helps restore healthy bodily tissue. MSM is often taken to alleviate arthritis symptoms, including pain and swelling in the joints.
MSM works by supplying sulfur to your body, which is crucial for making other chemicals in the body. It’s often combined with glucosamine and chondroitin in joint health supplements.
Omega-3, Turmeric, etc
Omega-3 fatty acids and turmeric are both highly beneficial supplements for joint pain. Omega-3s are essential fats that our bodies cannot produce themselves. They have anti-inflammatory properties, making them a popular choice for those with joint pain caused by conditions like arthritis. Omega-3s are found in foods like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts but can also be taken as a supplement to ensure you’re getting enough.
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with potent anti-inflammatory effects that’s been studied for its potential to reduce joint pain and swelling. It’s often used in the treatment of osteoarthritis and arthritis. Turmeric can be incorporated into your diet through food, but supplements offer a more concentrated dose of curcumin.
Choosing the Right Joint Supplements

When choosing a joint supplement, you should focus on certain key ingredients, as mentioned earlier. Remember that the effectiveness of supplements can vary greatly, and while some people find significant pain relief with these products, others may not notice any difference. It’s also worth noting that supplements are not a replacement for a healthy diet and lifestyle. Therefore, it’s important to do your research and perhaps consult with a healthcare professional to ensure you’re choosing the most effective product for your specific needs.
Side Effects
While joint supplements can be beneficial, they may also have potential side effects. It’s important to note that everyone’s body reacts differently to supplements, and what works well for one person may not work well for another. Some possible side effects of commonly used joint supplements include stomach upset, constipation, diarrhea, headache, and skin reactions.
FAQ’s
Is there a joint supplement that really works?
Yes, there are joint supplements that have shown great health benefits, among them Chiropractor’s Choice Glucosamine.
Is turmeric better than glucosamine?
Both turmeric and glucosamine have their unique benefits when it comes to joint health, and they work best when they are combined in one product.
What vitamin are you lacking if your joints hurt?
Several factors can cause joint pain, and certain vitamin deficiencies may contribute to it. Pay attention to vitamin B3, vitamin C, vitamin E, and vitamin D deficiency.
Do I need omega-3 and glucosamine?
It’s beneficial to include both of them. Preferably, buy a product that includes omega-3 and glucosamine.
Is glucosamine better than omega-3?
When combined with omega-3 fatty acids, it’s suggested that improvements in joint health can be even better than when using glucosamine alone.
